
Hernia Surgery Laparoscopic vs Open
When fatty tissue or an organ pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding connective tissue or muscle wall, it causes a hernia. Hernias do not usually heal on their own. They tend to grow in size. They can cause life-threatening complications in rare cases. That is why doctors frequently recommend surgery. However, not all hernias require immediate treatment. It is determined by the size and severity of the symptoms. If it does not become symptomatic, it may not require any treatment. A surgical hernia repair involves using mesh to push the bulge back inside the body part that should contain it and keep it there.
Do I Need Hernia Surgery?
Your doctor will likely recommend it if any of these things happen:
. Tissue (such as the intestine) becomes trapped in the abdominal wall. This is called incarceration. If left untreated, it may lead to strangulation. That’s when the blood supply to the tissue gets cut off.
. The hernia becomes strangulated. This can cause permanent damage and is a surgical emergency. Strangulated organs, usually your intestines, will die, and if not removed quickly, you can become seriously ill. Call your doctor right away if you have a fever or nausea, sudden pain that gets worse, or a hernia that turns red, purple, or dark.
. The hernia causes pain or discomfort, or it’s growing larger.
You may be able to wait to have surgery if:
. Your hernia goes away when you lie down, or you can push it back into your belly. This is called a reducible hernia.
. It’s small, and causes few — or no — symptoms (these may never need surgery)
Talk to your doctor. They’ll monitor your hernia during your yearly physical.
Nearly all children and adults can have hernia surgery. If you’re seriously ill or very frail, you may choose not to have an operation. Your doctor can help you weigh the benefits of the procedure against your ability to recover.
Hernia Surgery Types
Your doctor can remove your hernia in one of two ways. Both are done at a hospital or surgery center. You’ll usually go home within a few days. In many cases, you’ll be able to go home the same day as your procedure.
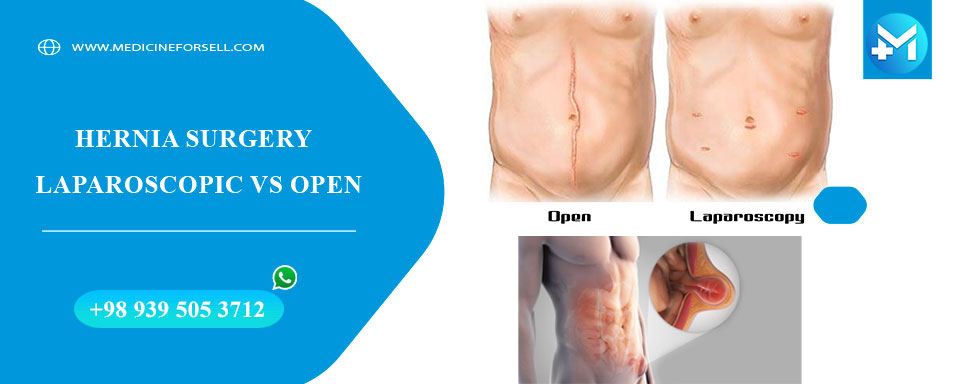
. Open surgery:
You will receive general anesthesia before having open surgery. The surgeon makes a cut (incision) to open your skin. They’ll gently push the hernia back into place, tie it off, or remove it. Then they’ll close the weak area of the muscle — where the hernia pushed through — with stitches. For larger hernias, your surgeon may add a piece of flexible mesh for extra support. It’ll help keep the hernia from coming back.
. Laparoscopic surgery:
In this surgery, your abdomen is inflated with a harmless gas. This gives the surgeon a better look of your organs. They’ll make a few small incisions (cuts) near the hernia. They’ll insert a thin tube with a tiny camera on the end (laparoscope). The surgeon uses images from the laparoscope as a guide to repair the hernia with mesh. For laparoscopic surgery, you’ll receive general anesthesia. Recovery is usually faster with laparoscopic surgery: On average, patients are back to their normal routine a week sooner than with open surgery.
What kind of surgery you’ll need often depends on the size, type, and location of your hernia. Your doctor will also consider your lifestyle, health, and age.
Hernia Surgery Risks
This type of operation is normally very safe. But like all surgeries, having your hernia removed comes with a number of possible complications. They include:
. Infection of the wound
. Blood clots: These can develop because you’re under anesthesia and don’t move for a long period of time.
. Pain: In most cases, the area will be sore as you heal. But some people develop chronic, long-lasting pain after surgery for a groin hernia, for example. Experts think the procedure may damage certain nerves. Laparoscopic surgery may cause less pain than an open procedure.
. Recurrence: The hernia could come back after the surgery. Research shows that using mesh can reduce your risk of this happening by half.
Non-Surgical Hernia Treatments
Your physician may recommend that you wear a corset, binder, or truss. These supportive undergarments apply gentle pressure on the hernia and keep it in place. They may ease discomfort or pain. They’re used if you aren’t able to have surgery, or for temporary relief before your procedure. Only use these garments under your doctor’s supervision.
Hernia Surgery Cost
While we encourage you to contact our support team to get a more precise estimate of the final costs, it’s worth noting that an average cost of hernia surgery in Iran starts from $1,400. Keep in mind that the cost of hernia surgery is considerably higher in almost all other places. For instance, its around $7,750 in the U.S., it begins at $2,000 in Europe and $2500 in Turkey and it ranges from $900 to $1500 in India.
Hernia Surgery FAQ
When might I need emergency surgery?
Seek immediate medical attention if there are signs that your hernia has become stuck or strangulated, which can be life-threatening and usually requires emergency surgery. Signs of this condition include:
. A hernia bulge that is suddenly larger than before
. A hernia bulge that used to go back inside the abdomen but no longer does
. Fever
. Redness in the area of the hernia
. Sudden or severe pain or tenderness in the area of the hernia
. Symptoms of intestinal obstruction, such as abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting
What type of anesthesia should I receive for surgery?
Several anesthesia options may be discussed with your anesthesiologist, a medical doctor who specializes in anesthesia, pain management, and critical care medicine:
. Local anesthesia with sedation, also referred to as local with monitored anesthesia care, or MAC. This is the most frequently used option. Local anesthesia is usually administered as a one-time injection of medicine that numbs a small area of the body. Sedation relaxes you and is usually administered and adjusted through an IV placed in your arm. The level of sedation can range from minimal (you’ll feel drowsy but able to talk) to deep (you probably won’t remember the procedure).
. Nerve block and sedation. This might be used for inguinal or femoral surgeries, especially if the patient has severe heart or lung disease that precludes the use of general anesthesia. Nerve blocks involve the injection of an anesthetic into specific nerves to block pain signals.
. Spinal block and sedation. This less frequently used option numbs the body from the waist down. The medication for the spinal block is injected through a needle inserted in the lower back into the spinal canal.
. General anesthesia. This type of anesthetic renders you completely unconscious. It also impairs your breathing, so a breathing tube, ventilator, and inhalation anesthetic are used.
Discuss the options with the anesthesiologist assigned to your surgery. Anesthesiologists are experts in determining the safest and most effective anesthesia for a particular patient. Although they consider surgeon and patient anesthesia preferences, the type and size of the hernia could preclude some options. For example, general anesthesia is required if the surgeon needs to use a scope during the surgery or if the hernia is particularly large.
The anesthesiologist should ask you about your prior experience with anesthesia and about any anesthesia reactions among your family members, going back multiple generations if possible. You should also be asked about your current health and your health history, including any chronic pain that could make it difficult for you to remain comfortable under sedation instead of general anesthesia.
Let the anesthesiologist know if you use marijuana, CBD products, or other substances, as these can affect the type and amount of anesthesia you can safely receive. You may also be advised to temporarily stop using CBD in the days leading up to and after surgery because of its potential to increase the risk of bleeding.
How can I reduce and manage pain after hernia surgery?
Hernia surgeries typically do not cause a high level of postoperative pain, and most pain can be managed with medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol or other brands) and ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, etc.). These pain relievers can be supplemented with opioids, although this often is not necessary.
Limiting the use of opioids helps avoid negative side effects, including problems urinating after hernia surgery, which have been known to occur in a minority of patients after inguinal hernia repair. Postoperative urinary retention occurs most often in people over age 50, especially males. Taking medications as directed prior to surgery, including medicines for benign prostatic hyperplasia, which is caused by enlargement of the prostate, also helps prevent postoperative urinary retention.
Under medical direction, measures might also be taken before surgery to limit postoperative pain and nausea, such as taking acetaminophen for pain and a small dose of promethazine to prevent nausea. Consult your anesthesiologist about whether these are appropriate options for you.
How soon can I resume normal activities after hernia surgery?
Your surgeon will provide you with a specific plan but may not be able to give you an exact time frame in advance. Doctors usually cannot fully diagnose the severity of a hernia until they perform the surgery.
Hernia procedures are usually outpatient surgeries. In general, the sooner you can start moving afterward, the better. This movement helps prevent constipation and blood clots. Be sure to adhere to the doctor’s instructions about what you can lift, how to lift, and how long to remain on any restrictions; some may be permanent.
Can hernia surgery result in chronic pain?
Chronic pain affects about 10% of inguinal hernia patients after surgery, according to the International Guidelines for Groin Hernia Management. The guidelines define chronic pain as bothersome moderate pain impacting daily activities for at least three months.
The guidelines also indicate that chronic pain is a higher risk for patients who are young or female, experience high preoperative or high early postoperative pain, have a recurrent hernia, or undergo open repair. Mesh can also cause or contribute to chronic pain. Studies indicate that the risk of chronic pain is less with laparoscopic repair than with open repair, but the type and size of the hernia sometimes preclude the laparoscopic option.
If you suffer from chronic pain, consult with a pain management specialist to consider options such as medication and nerve blocks. Many anesthesiologists are pain management specialists.
About Medicine for sell
Medicine for sell is an online medical tourism platform where you can find the best doctors, surgeons and specialists in Iran. The price of Hernia Surgery in Iran can vary according to each individual’s case and will be determined by an in-person assessment with the doctor.
For more information about the cost of Hernia Surgery in Iran and to schedule an appointment in advance, you can contact Medicineforsell consultants via WhatsApp number 0098 9395053712. This service is completely free.
Source:
https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/need-surgery-hernia
https://www.asahq.org/madeforthismoment/preparing-for-surgery/procedures/hernia-surgery/